
Transnasal Endoscopic Surgery is a minimally invasive technique used to access deep-seated areas of the brain and skull base through the nasal passages.
This approach eliminates the need for large scalp or skull incisions, reducing trauma, scarring, and recovery time. It is commonly used to treat pituitary tumors, skull base lesions, and certain cysts while preserving vital neurological functions.
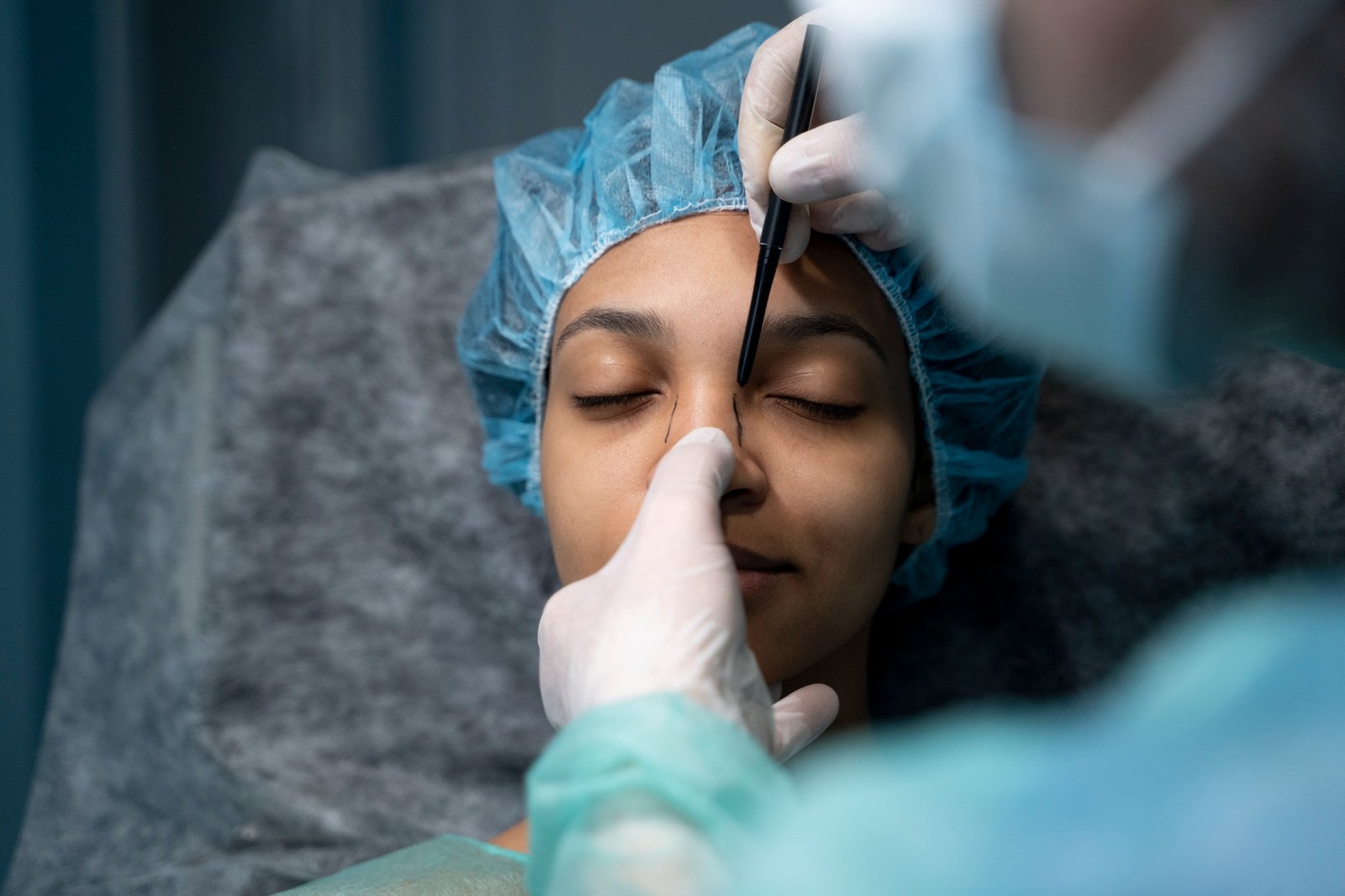
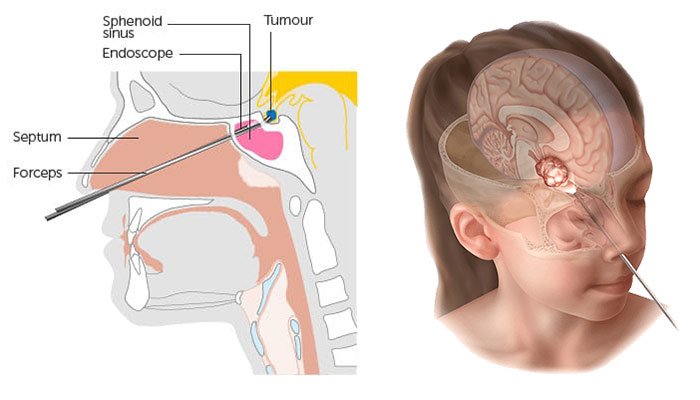
Before surgery, patients undergo thorough diagnostic imaging such as MRI, CT scans, and angiography to map the lesion and surrounding anatomy. Surgeons carefully plan the approach to ensure minimal disruption of surrounding tissue and maximal removal of the target lesion.
This meticulous pre-surgical assessment enhances safety, accuracy, and surgical outcomes.
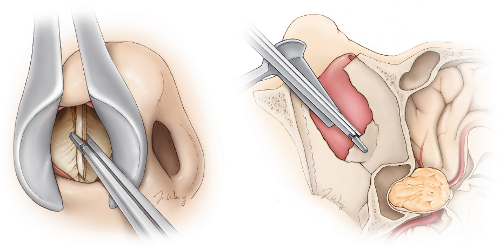
During transnasal endoscopic surgery, surgeons use a high-definition endoscope combined with microsurgical instruments to operate through the nasal passages. Advanced neuronavigation and intraoperative monitoring allow precise targeting of the tumor or lesion while protecting critical structures. This technique minimizes bleeding, reduces hospital stay, and allows patients to recover faster compared to traditional open surgery.
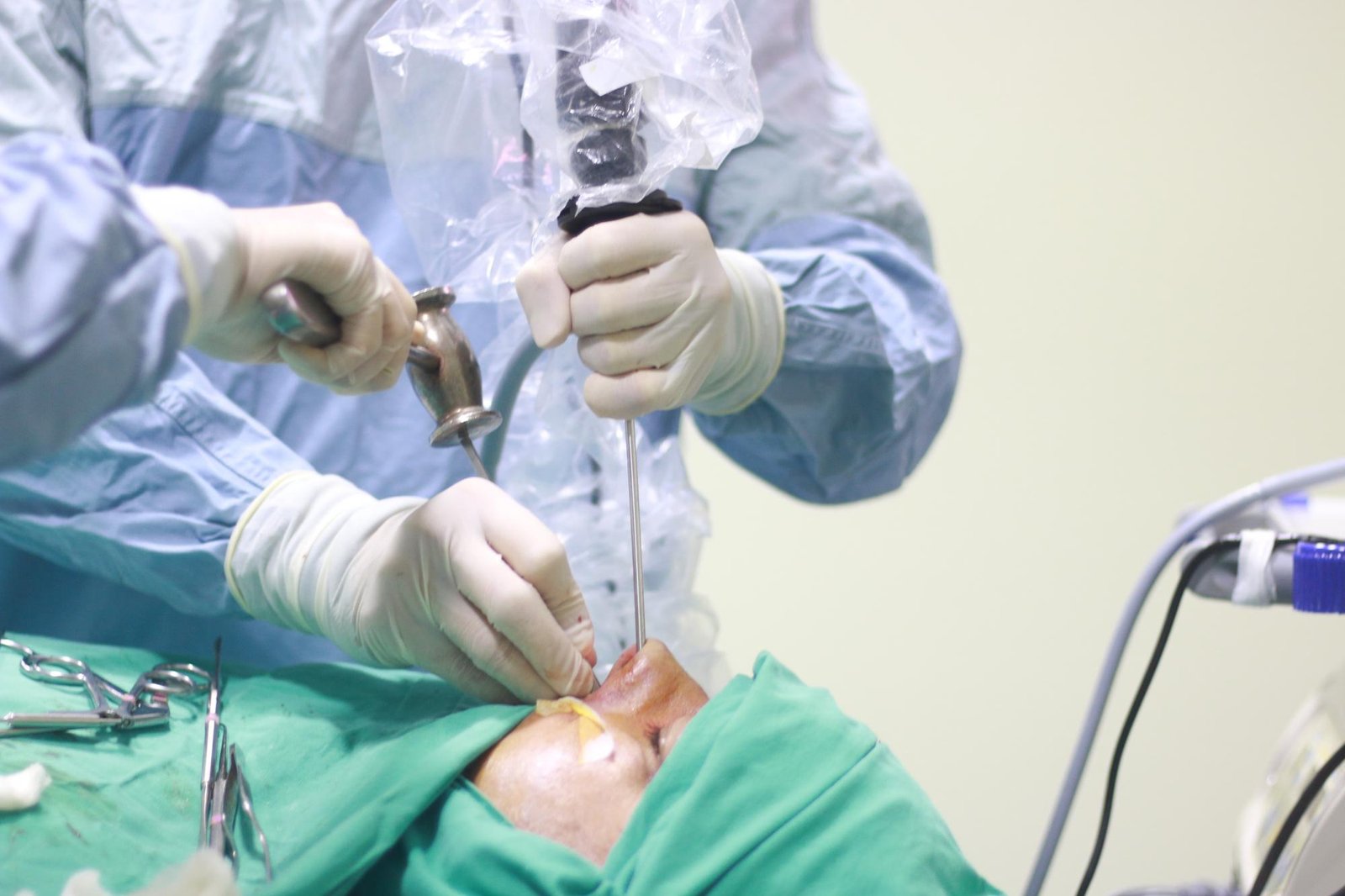
After surgery, patients receive specialized post-operative care including monitoring, pain management, and follow-up imaging to track recovery. Rehabilitation, if needed, focuses on restoring neurological function and overall well-being.
With its minimally invasive nature, transnasal endoscopic surgery ensures quicker recovery, minimal discomfort, and effective treatment outcomes for patients.
