
Neuroendoscopic surgery is a modern, minimally invasive procedure used to treat various brain and spinal conditions through small openings. By using an endoscope—a thin, flexible tube with a camera—surgeons can access deep areas of the brain with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues.
This approach reduces surgical trauma, shortens hospital stays, and speeds up recovery. It is commonly used for conditions like hydrocephalus, pituitary tumors, intraventricular tumors, and certain cysts.
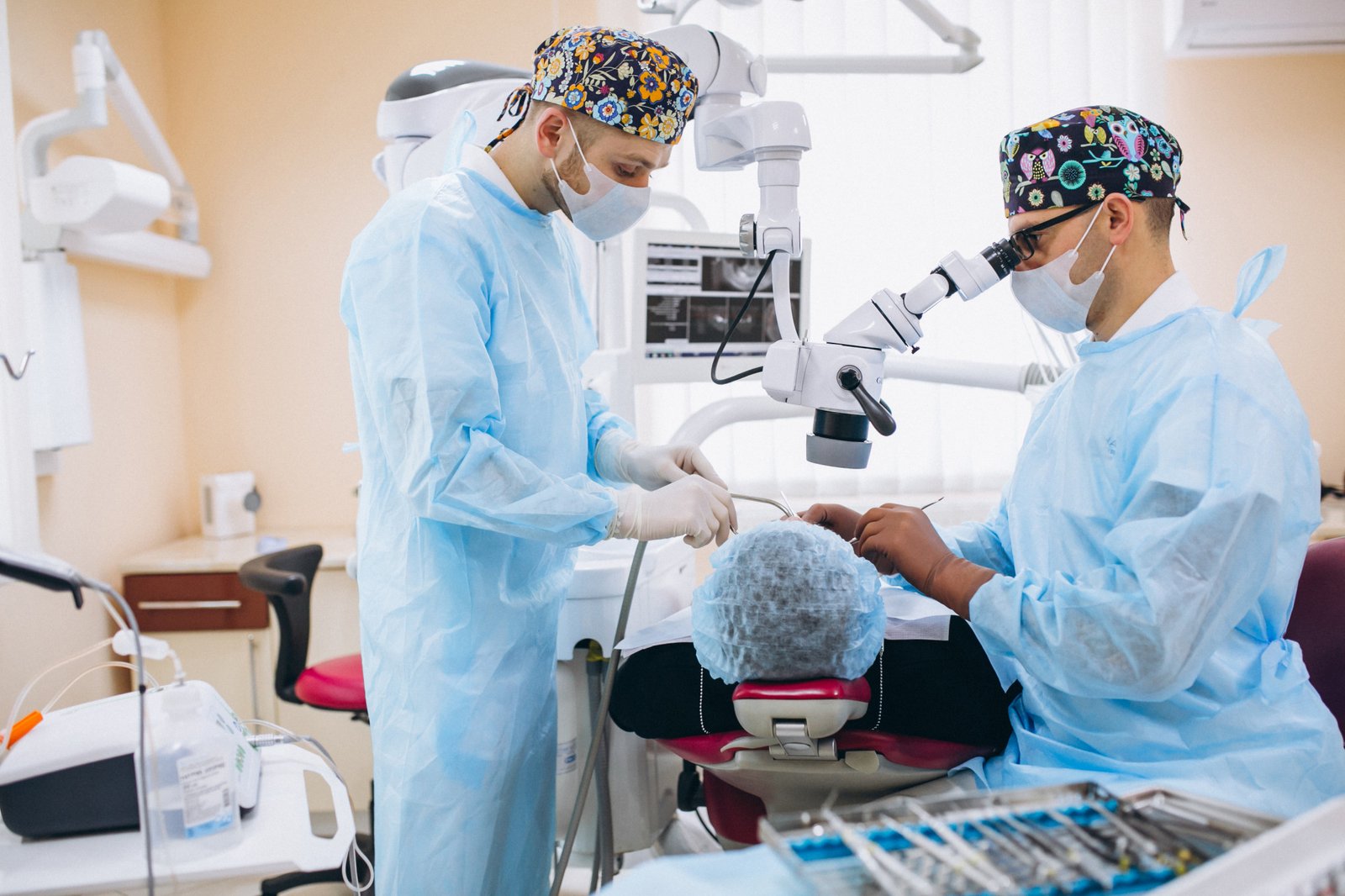
Before undergoing neuroendoscopic surgery, patients receive thorough diagnostic assessments including MRI and CT scans to map the exact location and nature of the condition.
The surgical plan is customized based on the patient’s specific needs, ensuring the safest and most effective route to the targeted area. This careful planning minimizes risk, enhances surgical accuracy, and supports the best possible results.
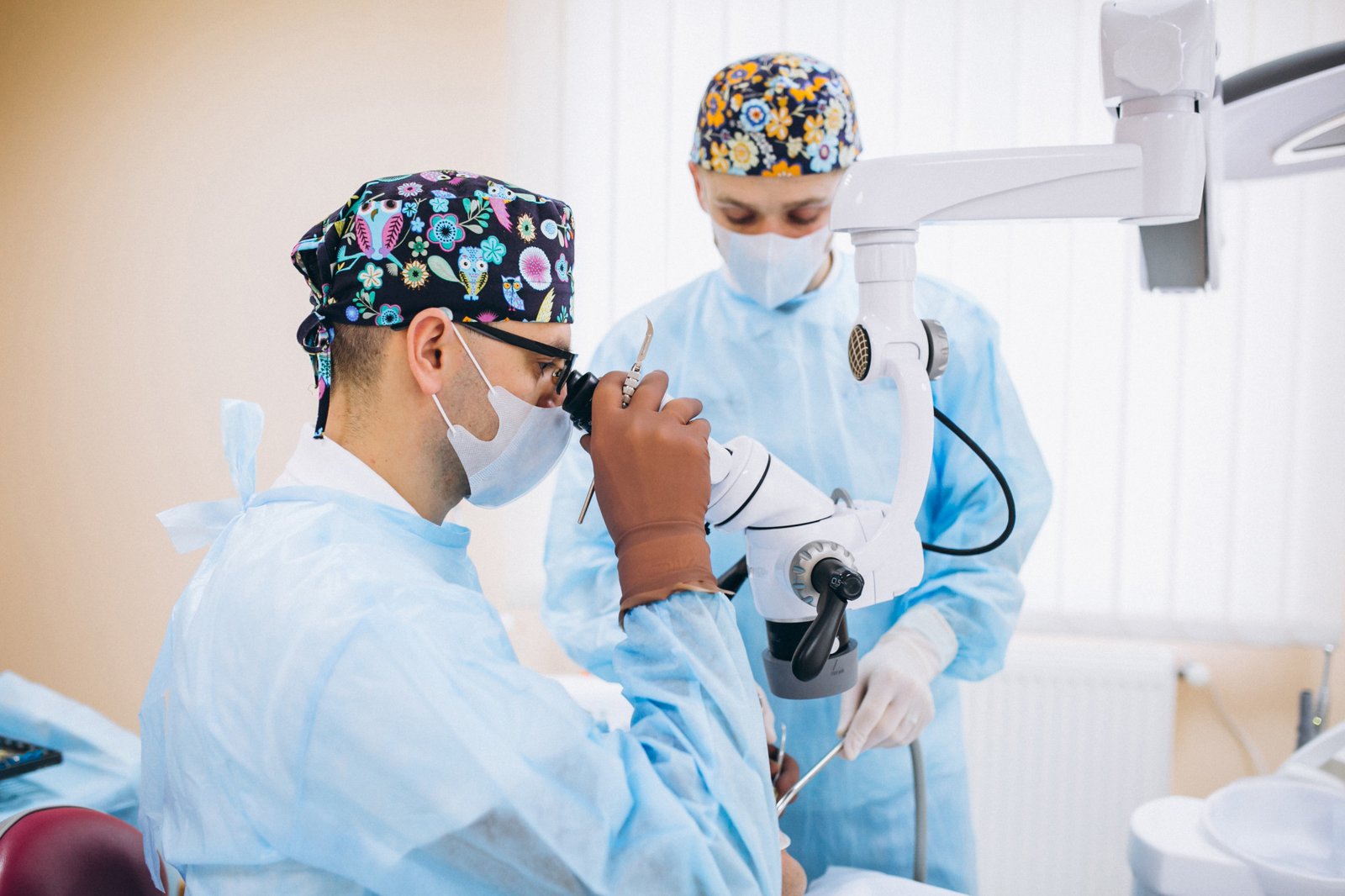
During the procedure, surgeons insert the endoscope through a small incision, allowing real-time visualization of the surgical area on a high-definition screen. Special micro-instruments are used alongside the endoscope to remove tumors, relieve fluid buildup, or correct structural abnormalities.
Because this method avoids large openings, it reduces bleeding, infection risk, and recovery time—making it a safer alternative to traditional brain surgery.
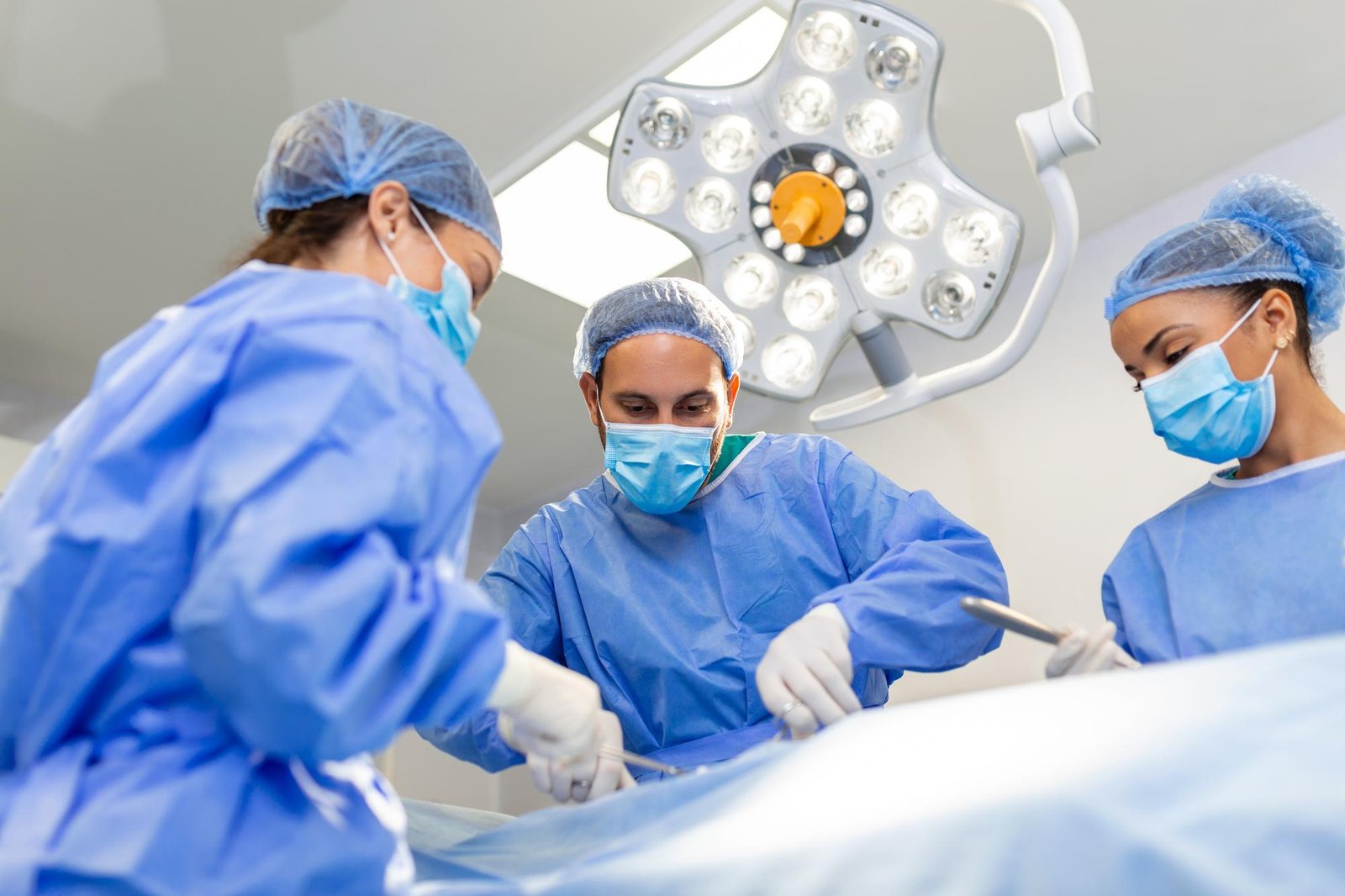
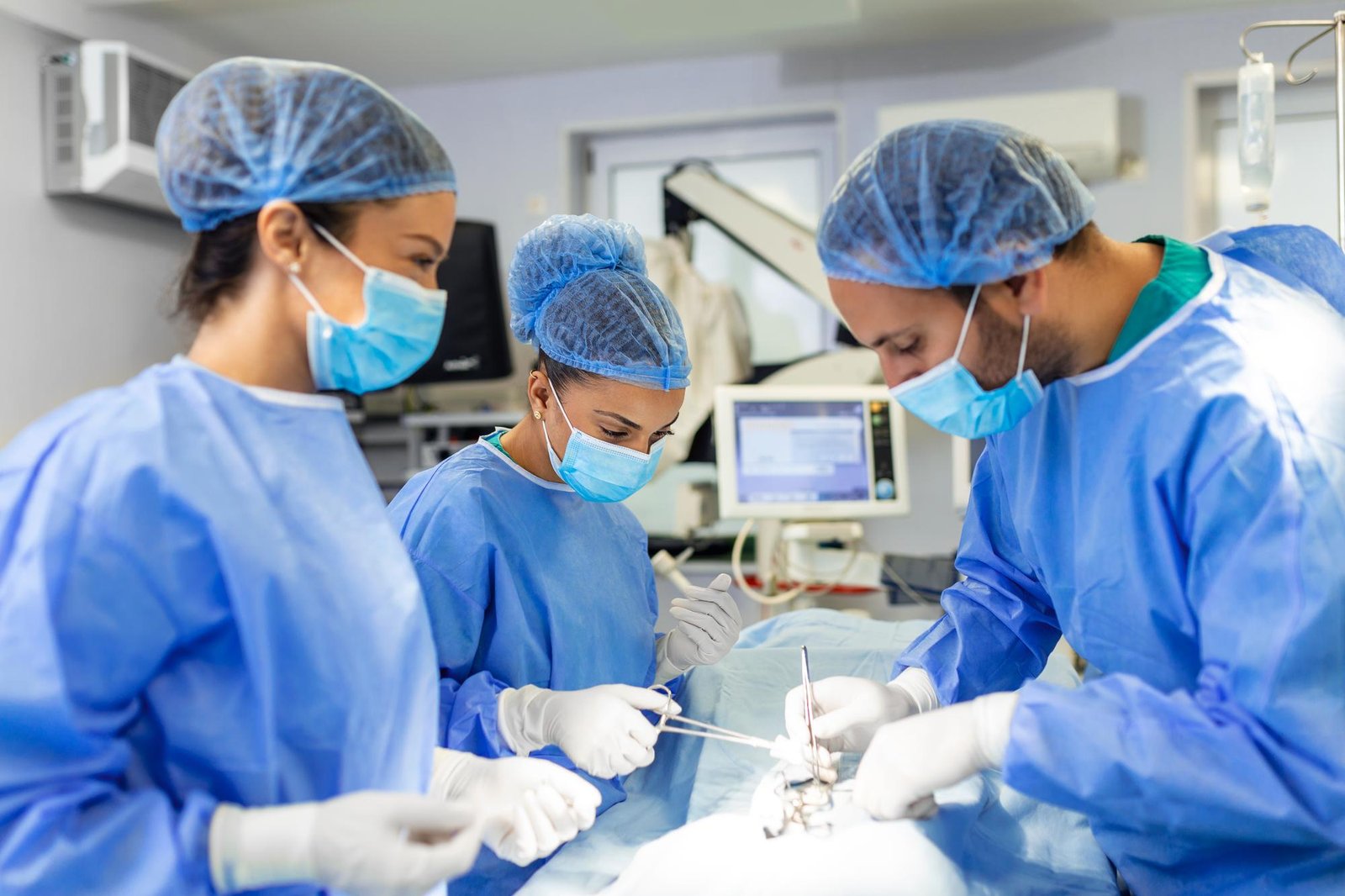
Following neuroendoscopic surgery, patients typically experience shorter hospital stays and quicker return to normal activities. Comprehensive post-operative care includes monitoring, rehabilitation, and follow-up imaging to ensure optimal healing.
With its minimal invasiveness and excellent outcomes, neuroendoscopic surgery offers patients a safe, effective, and comfortable path toward recovery and long-term neurological health.
